1. Shut down your system
2. Turn off your computer completely.
3. Now remove the power cable and battery if applicable. The battery removal step applies only to laptops when it's possible to remove the battery. To see how to remove the battery, refer to your owner's manual.
4. Discharge residual power if this is a laptop installation. If your laptop has a removable battery, remove it, and hold the power button for five seconds to discharge any electricity left in the system.
5. Open the computer case or user accessible bay
6. Touch an unpainted metal surface to ground yourself. This protects your computer's components from the static electricity that's naturally present in your body - grounding is an extra safeguard.
7. Locate the M.2 PCIe slot. This slot is usually easy to find in desktops, but in laptops the location will vary - it's typically under the bottom panel, or under the keyboard. Refer to your owner's manual for the exact location, as every system looks slightly different.
8. Insert the SSD. Depending on your computer, there might be a heat sink or screw that needs to be removed prior to inserting your new NVMe PCIe SSD. To insert your PNY NVMe PCIe SSD, hold the SSD carefully by the sides. Do not touch the gold connector pins. Align the notches in the SSD with the ridges in the PCIe slot, then insert at a 30-degree angle. Do not force the connection.
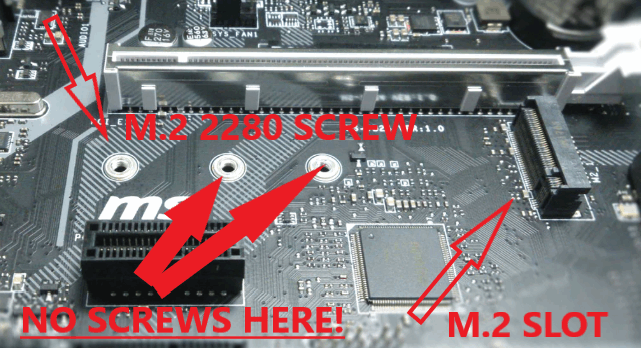
To secure the drive, it might be necessary to insert the screw into the provided mount on the motherboard. Do not over-tighten the screw. MAKE SURE you only use the mounting screw for the "2280" drive. This should be printed on your motherboard or this information will be provided in your motherboard owners manual. Please remove any screws that may be installed in the 2260 of 2242 mounts on your motherboard. Failure to do so will result in damage of your PNY M.2 2280 NVMe drive. Please refer to the picture below.
9. After the SSD is securely seated in the slot, put your computer back together and reconnect the battery if it was removed. Turn on your computer. Unless you removed your old storage drive in a previous step, the computer is booting from the old drive and you will need to enter your motherboard BIOS and change the boot order to the the new M.2 drive and then install your operation system or clone your existing drive to the new M.2 drive using cloning software of your choice.